Raoultella Ornithinolytica Pneumonie / Diseases Free Full Text Carbapenemase Producing Raoultella Planticola A Rare Cause Of Pneumonia And Bacteremia Html
Representatives are Gram-negative capsulated nonmotile rods. Klebsiella pneumoniae produces no histamine.
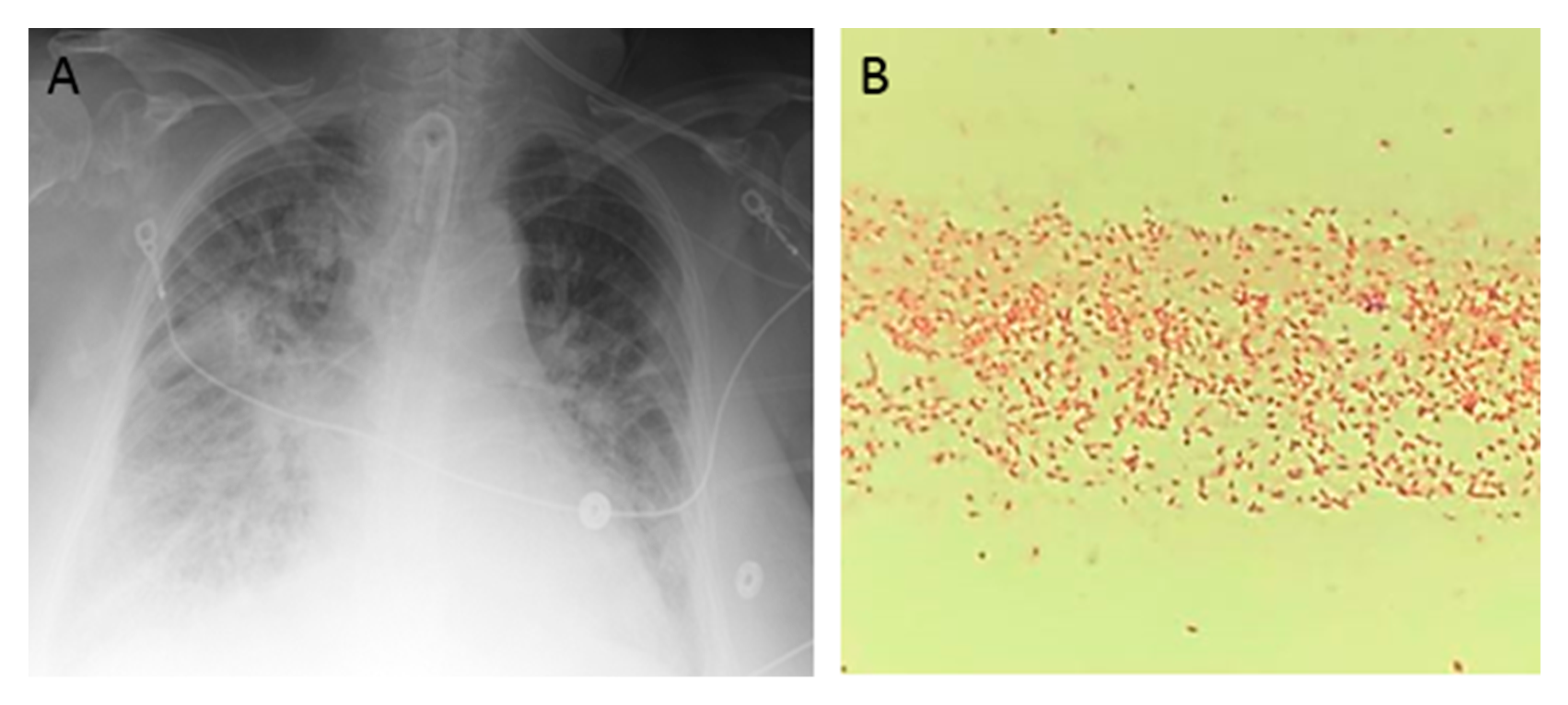
Diseases Free Full Text Carbapenemase Producing Raoultella Planticola A Rare Cause Of Pneumonia And Bacteremia
Kanki M 1 Yoda T Tsukamoto T Shibata T.

Raoultella ornithinolytica pneumonie. Ornithinolytica is the only species within the genus which has the ability to produce ornithine decarboxylase. Plants water soil and insects. Ornithinolytica that has been reported in the literature.
Planticola had not been reported as an HPB except in the case of strain ATCC 43176 4 10 11. Infections with Raoultella ornithinolytica have recently been reported more frequently in the medical literature. Since the late 2000s there has been an increase in case reports of human Raoultella.
Here we report the first two cases of ventilator-associated pneumonia VAP in trauma patients caused by Raoultella ornithinolytica. Raoultella planticola and Raoultella ornithinolytica strains are histamine producers. In general the incidence of Raultella ornithinolytica is underestimated due to the imprecision of conventional phenotypic identification methods generating uncertainties as to its pathogenicity Ponce-Alonso et al 2016 mainly due to the similarities with species of the Klebsiella genus such as K.
They are mainly found in aquatic envi-ronments plants and soil whereas it is rare to find them in clinical samples mostly the last two species. Raoultella ornithinolytica is an encapsulated Gram-negative oxidase-negative catalase-positive aerobic non-motile rod that belongs to the Enterobacteriaceae family. These bacteria are found in the natural environment.
Ventilator associated pneumonia caused by Raoultella ornithinolytica in two immunocompetent trauma patients. - case report written by D V Smith B A Boucher published on May 7 2018Main subjects. This bacterium was initially classified in the genus Klebsiella as Klebsiella ornithinolytica until the creation of the genus Raoultella.
Ornithinolytica was also classified in the genus Raoultella. Ornithinolytica sepsis and purpura fulminans in a preterm female baby. These bacteria primarily Klebsiella pneumoniae and to a lesser extent Klebsiella oxytoca and Raoultella ornithinolytica are responsible for various public health problems including respiratory and urinary tract infections liver abscesses and septicemia Brisse et al 2006.
PDF Infections with Raoultella ornithinolytica have recently been reported more frequently in the medical literature. Are opportunistic bacteria which usually cause infections of the biliary tract pneumonia and bacteraemia in oncologic and with lower immunity patients. The genus Raoultella was established in 2001.
Beranda Raoultella Ornithinolytica Pneumonie. Similarly five strains of Raoultella ornithinolytica formerly Klebsiella ornithinolytica were isolated from fish as new HPB. This pathogen has the potential.
Our case is the second newborn case of human infection by R. However the incidence of isolation of R. Raoultella planticola and Raoultella ornithinolytica are the most frequently encountered human pathogens among the genus Raoultella.
Oxytoca by commercialized systems were later correctly identified as Raoultella planticola formerly Klebsiella planticola by additional tests. This pathogen has the potential to cause many types of infections including pneumonia. Given the shortcomings of available technology for species identification in the clinical microbiology laboratory are practically indistinguishable.
Ventilator associated pneumonia caused by Raoultella ornithinolytica in two immunocompetent trauma patients. Klebsiella pneumoniae and Klebsiella oxytoca are the best-known HPB in fish. An Atypical Case Of Raoultella Planticola Urinary Tract Infection Infectious Diseases amna-anderson1 Agustus 20 2021 Raoultella Ornithinolytica Pneumonie.
Ornithinolytica is one of the three species of Raoultella. Raoultella ornithinolytica Raoultella planticola Raoultella terrigena and Raoultella electrica. Species of Raoultella and Klebsiella share many ecological biochemical clinical and microbiological features.
However 22 strains of HPB from fish first identified as K. Histamine fish poisoning is caused by histamine-producing bacteria HPB. Oxytoca had been shown to be HPB in several reports whereas R.
Raoultella ornithinolytica is a Gram-negative encapsulated aerobic bacillus belonging to family EnterobacteriaceaeIt is an extremely rare causative organism of infections in humans.
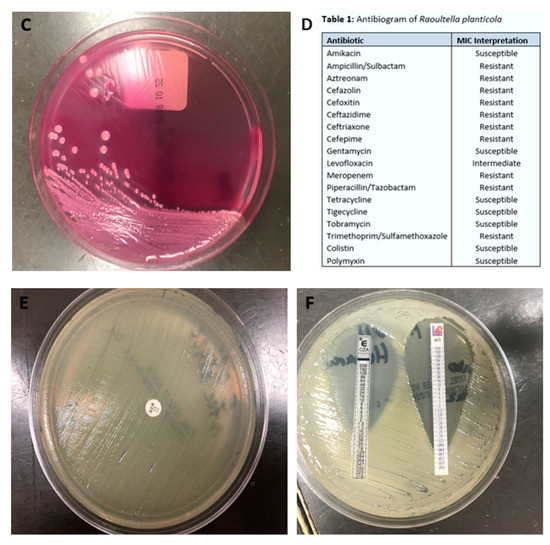
Diseases Free Full Text Carbapenemase Producing Raoultella Planticola A Rare Cause Of Pneumonia And Bacteremia Html

Pdf Raoultella Ornithinolytica Diagnosed In A Neurointensive Patient A Rare Case With Recovery Without Antibiotics

A Rare Cause Of Infection Raoultella Planticola Emerging Threat And New Reservoir For Carbapenem Resistance Semantic Scholar

A Rare Instance Of Hospital Acquired Pneumonia Caused By Coinfection With Raoultella Planticola Consultant360

Susceptibility Profile Of Raoultella Ornithinolytica Download Table

A Rare Instance Of Hospital Acquired Pneumonia Caused By Coinfection With Raoultella Planticola Consultant360

Pdf Raoultella Ornithinolytica Bacteremia In Cancer Patients Report Of Three Cases

Tuberculosis And Respiratory Diseases

An Atypical Case Of Raoultella Planticola Urinary Tract Infection Infectious Diseases

Ventilator Associated Pneumonia Caused By Raoultella Ornithinolytica In Two Immunocompetent Trauma Patients Semantic Scholar

Pdf A Case Of Pneumonia Caused By Raoultella Planticola

Pdf Resistant Raoultella Ornithinolytica Bacteremia In A Patient With New Acute Myeloid Leukemia

Raoultella Ornithinolytica Emergence And Resistance Idr

Pdf Emergence Of Raoultella Ornithinolytica Isolated From Chicken Products In Alexandria Egypt

Raoultella Ornithinolytica Emergence And Resistance Idr

A Rare Case Of Raoultella Planticola Pneumonia An Emerging Pathogen Sciencedirect

Emerging Role Of Raoultella Ornithinolytica In Human Infections A Series Of Cases And Review Of The Literature Sciencedirect

